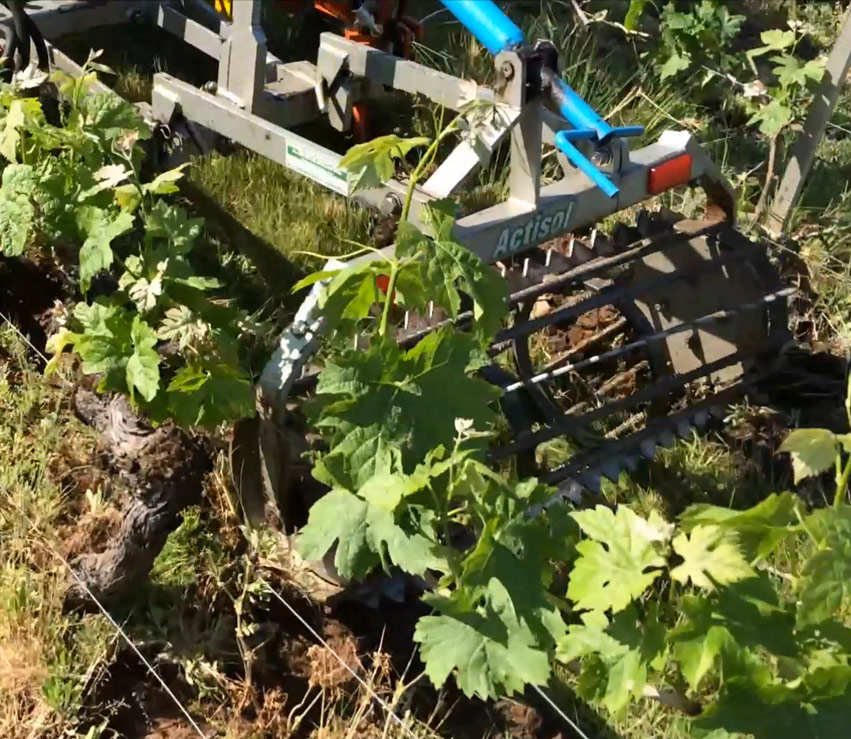
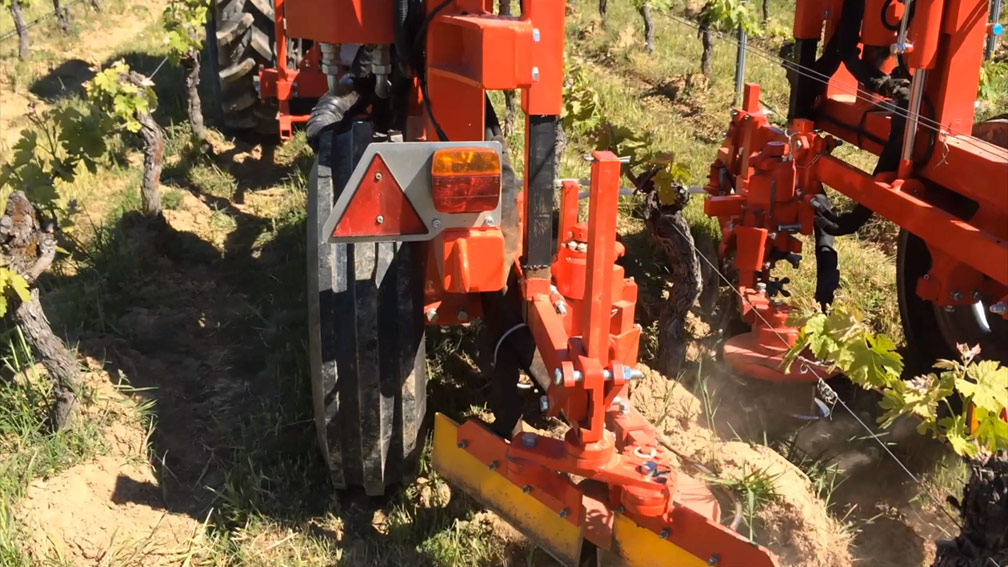
The soil is also a complex biological ecosystem where macro and micro-organisms that structure the soil live in symbiosis, breaking down vegetal or organic detritus and transforming them into stable humus. Among others, these organisms include earthworms, insects, fungi, algae and bacteria…
The final and decisive phase for feeding a plant involves fungi named Mycorrhiza that transform organic elements into soluble mineral elements in water which can then be absorbed by the root.
Any action taken by humans leads to consequences upon this ecosystem. Every year, active substances contained in chemical weed killers are withdrawn from sale (due to their carcinogenic risk). Some of these are not broken down and their residues are found in the soil or water, where they continue to accumulate.
At present, the fate of glyphosate is to be decided by the European Commission.